OBJECTIVE
As current MDIs contain hydrofluorocarbon propellants, it would be beneficial to find ways to reduce carbon emissions without compromising patient safety.
This lab study investigated a way to optimize the modelled lung dose per actuation while at the same time minimizing the carbon emissions from the MDI
METHOD
Two different salbutamol 100mcg MDIs were investigated, Ventolin† (GSK) and Teva†- salbutamol (Teva).
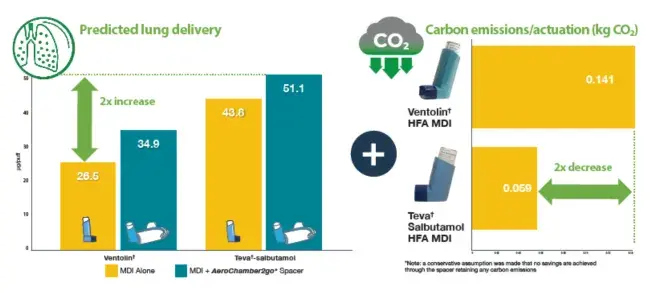
Each was tested alone and combined with an AeroChamber2go* Spacer (TMI), designed for on the go use with reliever medications.
Fine particle mass (< 4.7 microns), therefore the mass of drug in the size range potentially available for lung delivery, was determined using an abbreviated cascade impactor, performed with no delay following actuation, and HPLC assay.
Carbon emissions per actuation were also determined
RESULTS
More efficient delivery of inhaler medication leads to less use of medication and therefore less carbon footprint. See the results below:

CONCLUSION
The use of the new portable spacer with a lower carbon emitting salbutamol MDI has the potential to improve lung delivery and reduce carbon emissions.
In combination, the selection of the Teva†- salbutamol MDI delivered using the AeroChamber2go* Spacer could potentially reduce the number of actuations required for patient relief of symptoms, which could help contribute to an up to 4.6x reduction in the carbon emissions compared to using a Ventolin† MDI product alone.
